DAO: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
m (→Examples) |
||
| (40 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A DAO is the fundamental unit of consideration in the [[DAO Governance Framework project|DGF project]]. | A [[wikipedia:Decentralized_autonomous_organization|DAO]] is a decentralized autonomous organization. A DAO is the fundamental unit of consideration in the [[DAO Governance Framework project|DGF project]]. Commonly, a DAO is a for-profit group run using P2P tools, such as blockchain smart contracts, to automate its governance. | ||
The typical DAO we consider in the DGF project may be thought of as a decentralized, global corporation that uses the internet and computing technology, to make business transactions and to govern itself. As such, a DAO is a community-driven, for-profit cooperative that relies on programming to stay organized. | |||
However, corporations are not the perfect image to conjure when thinking about what a DAO is. In some ways, an open DAO is more like a continual marketplace, where anyone can join or leave at any time. The major difference from a traditional marketplace is that there is no central person or body in charge of a DAO. This type of marketplace is run by the very people who participate in it, with fluid changes in relative power based on participation. | |||
Under [[DAO Governance Framework|DGF]], in a for-profit DAO the workers get paid directly after a [[DAO Governance Framework#DGF workflow|review period]] where the other workers have a chance to evaluate whether the work was up to their group standards. The standards are set by the workers directly through DGF [[governance]]. | |||
{| | |||
== Conceptual overview == | |||
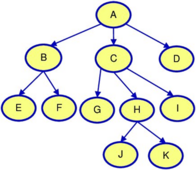
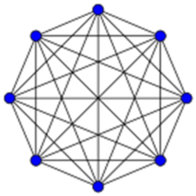
[[wikipedia:Decentralization|Decentralized]] means the opposite of centralized. An ideal centralized organization has a completed pyramidal-hierarchical power structure with a single ruler on top (Figure 1a) which dictates authority, distinguishing those above from those below. Perfect decentralization would be absolutely flat (Figure 1b). Imagine a radical direct democracy, where every decision is made with consensus by the entire membership, without fixed roles of authority. | |||
{| | |||
|+ | |+ | ||
|[[File:CentralizedHierarchyGraph.png| | |[[File:CentralizedHierarchyGraph.png|Centralized|right|196x196px]] | ||
|[[File:DecentralizedGraph.png| | |[[File:DecentralizedGraph.png|Decentralized|right|196x196px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
Figure 1: | ''<small>Figure 1: Centralized vs decentralized – hierarchical vs. flat power</small>'' | ||
Autonomous means the group [[Governance|governs]] itself. A DAO is not subject to direct control from outside the group. | |||
A DAO being an organization, means it consists of a coherent collection of members. Coherent means its members cooperate toward a common socio-economic goal. They follow a common set of protocols designed to serve their common [[Transcendental values|values]]. | |||
The term for the technology that enables decentralized organization is [[wikipedia:Peer-to-peer|peer-to-peer technology]]. P2P tech (see ''Main Article: [[P2P technology]]'') consists primarily of the internet, zero-knowledge proofs (including [[wikipedia:Public-key_cryptography|public-key]] digital signatures), [[wikipedia:Hash_function|hash functions]] (a universal tool for organizing data and error-correcting), and the software architecture of [[wikipedia:Blockchain|blockchains]] and [[wikipedia:Distributed_hash_table|distributed hash tables]]. | |||
== | DGF can be applied to build any type of DAO, but the primary concern of the DGF project is to create the governance structure for the most difficult type to build—a profit-centered, open-source, democratically-governed network which is open to pseudonymous, international members—''primary DAOs''. | ||
The following qualities maximize the effectiveness of a DAO. A DAO which embodies these qualities is called a | == Primary DAOs == | ||
The following qualities maximize the effectiveness of a DAO. A DAO which embodies these ideal qualities is called a ''primary DAO''. In the context of DAO building, let us carefully explain and justify all these terms: | |||
1. Openness | 1. Openness | ||
| Line 40: | Line 43: | ||
=== Openness === | === Openness === | ||
A DAO being '''open''' means its rules for accepting new membership is unrestrictive—everyone in the world has equal access to join, an equal opportunity to gain power, and an equal freedom to leave (while taking much of their personally accumulated value with them). It is preferable that a DAO adopt these properties of openness for two primary reasons. | A DAO being '''open''' means its rules for accepting new membership is unrestrictive—everyone in the world has equal access to join, an equal opportunity to gain power, and an equal freedom to leave (while taking much of their personally accumulated value with them).<ref>Open is synonymous with permissionless in public blockchains.</ref> It is preferable that a DAO adopt these properties of openness for two primary reasons. | ||
[[File:NetworkEffect2.png|border|right|412x412px|Network effect]] | |||
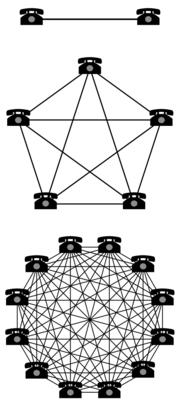
First, an open network encourages greater growth | First, an open network encourages greater growth. Combined with the network effect, this means a decentralized group grows in power faster than a centralized organization as its membership increases if communication is effective. To understand the '''network effect''', notice how <math>n</math> members don’t merely have <math>n</math> connections, they have <math>1+2+...+(n-1)=\frac{1}{2} (n^2-n)</math> individual connections. Connections grow quadratically with membership. A group of members also has an exponential number <math>2^n</math> of potential subgroups. Each subgroup of size <math>m</math> has <math>m!</math> different role assignments. Etc. As a group grows, there is more talent and more knowledge with quadratically more connections and exponentially more arrangements to foster more powerful collaboration. A decentralized organization with effective communication leverages the available energy of its members more effectively than a centralized organization.<ref>One of the major reasons centralized groups have been more competitive against decentralized groups in the past is that the tree structure of a hierarchy is the most efficient means of communication. It eliminates all redundancy. With contemporary information technology, however, we can now communicate practically with maximum redundancy. Everyone in a group of practically any scale can broadcast to and monitor the entire group.</ref> An open DAO leverages the available energy of the entire population more effectively than a closed DAO. This network effect is a major reason that decentralized organizations can be superior to centralized organizations, because a rigid hierarchy is limited to a single power structure for organizing its members to achieve all the tasks it will ever perform. When the market changes, a centralized system is not as agile as a decentralized system for solving new problems. | ||
The second major reason openness is ideal is that it serves the social good. It is a matter of basic justice that all people in a society are given equal opportunity to participate in all of its institutions. People prefer not to participate in a group that does not serve their values, especially one that limits their opportunities to gain power in the group. More importantly, they should not be forced to participate. | The second major reason openness is ideal is that it serves the social good. It is a matter of basic justice that all people in a society are given equal opportunity to participate in all of its institutions. People prefer not to participate in a group that does not serve their values, especially one that limits their opportunities to gain power in the group. More importantly, they should not be forced to participate. | ||
However, openness is a major security risk that needs to be continually addressed. Equal opportunity to participate is essential, but the types of participation that are beneficial to the group are naturally limited. Members who behave poorly must lose some of their power in the group, lest the group be destroyed by selfish behavior which virally spreads until the group becomes completely disorganized. Corruption | However, openness is a major security risk that needs to be continually addressed. Equal opportunity to participate is essential, but the types of participation that are beneficial to the group are naturally limited. Members who behave poorly must lose some of their power in the group, lest the group be destroyed by selfish behavior which virally spreads until the group becomes completely disorganized. [[Corruption]] must be limited or it will multiply until it destroys the group. Therefore, to maintain openness, a DAO needs strong, automated, executive governance. | ||
=== Pseudonymity === | === Pseudonymity === | ||
| Line 72: | Line 73: | ||
=== Security === | === Security === | ||
Security is a constant concern in the design of an open-source protocol. Especially when the network is open to pseudonymous members. [[wikipedia:Byzantine_fault|Byzantine]] behavior in a decentralized network, is defined as actions which violate the majority agreed protocols. When there is no dictator ruling your platform, and you accept asynchronous distributed transactions entering from any node, it is impossible to achieve perfect intelligence about the state of the network, since Byzantine nodes can pass false messages in the gossip network. There are several theorems in computer science that govern what is possible when designing a protocol for distributing digital token rewards in a DAO. A famous example is the 66% non-Byzantine limit for the pBFT algorithm. In general, no decentralized system can survive forever in the face of 51% Byzantine actors. Therefore some restrictions to openness are necessary. | Security is a constant concern in the design of an open-source protocol. Especially when the network is open to pseudonymous members. [[wikipedia:Byzantine_fault|Byzantine]] behavior in a decentralized network, is defined as actions which violate the majority agreed protocols. When there is no dictator ruling your platform, and you accept asynchronous distributed transactions entering from any node, it is impossible to achieve perfect intelligence about the state of the network, since Byzantine nodes can pass false messages in the gossip network. There are several theorems in computer science that govern what is possible when designing a protocol for distributing digital token rewards in a DAO. A famous example is the 66% non-Byzantine limit for the pBFT algorithm. In general, no decentralized system can survive forever in the face of [[51% attack|51% Byzantine actors]]. Therefore some restrictions to openness are necessary. | ||
Another major security risk to a decentralized platform is a sock puppet attack. [[wikipedia:Sock_puppet_account|Sock puppets]] are multiple pseudonymous accounts that a single member creates and controls with separate passwords to hold digital tokens. The purpose of sock puppet accounts is to trick the network into believing the different pseudonymous identities represent multiple people. This eliminates any chance that a DAO without KYC protocols can achieve honest governance under simple one-person-one-vote democracy. Since anyone on the planet has equal opportunity to participate under a fabricated identity, a single actor can create countless sock puppet accounts to overwhelm the voices of honest members. Therefore, any DAO work model or governance design must account for this eventuality. The solution to fighting sock puppet attacks, is a weighted democracy which assign rewards and power based on carefully audited measures of positive contributions to the group. | Another major security risk to a decentralized platform is a sock puppet attack. [[wikipedia:Sock_puppet_account|Sock puppets]] are multiple pseudonymous accounts that a single member creates and controls with separate passwords to hold digital tokens. The purpose of sock puppet accounts is to trick the network into believing the different pseudonymous identities represent multiple people. This eliminates any chance that a DAO without KYC protocols can achieve honest governance under simple one-person-one-vote democracy. Since anyone on the planet has equal opportunity to participate under a fabricated identity, a single actor can create countless sock puppet accounts to overwhelm the voices of honest members. Therefore, any DAO work model or governance design must account for this eventuality. The solution to fighting sock puppet attacks, is a weighted democracy which assign rewards and power based on carefully audited measures of positive contributions to the group. | ||
=== Weighted Democracy === | === Weighted Democracy === | ||
A weighted democracy is a | A weighted democracy is a [[governance]] structure where the power to decide the protocols for the DAO is determined by vote (democracy), but the power of each person’s vote may be different (weighted). | ||
How is this weight of power determined? In most of the original functioning DAOs, power is dictated by ownership of the currency token. In that case plutocracy is the ''de facto'' governmental structure. Little reflection is needed before most new DAO architects reject this design. Instead the common solution is to build their | Democracy of some type is necessary to achieve decentralized organization because inasmuch as control is not distributed amongst the members widely, then the group is less decentralized. Decentralization can be more effective than centralization, when effectively utilized, for three main reasons: 1. power is given to the most appropriate servant, 2. information at the edge is revealed, 3. the processing power of the entire group is utilized ([[wikipedia:Linus's_law|with enough eyes, every problem is shallow]]). | ||
The weighting of the democracy is necessary in an open pseudonymous group, because it eliminates the threat of sock puppet attacks: 100 sock puppet accounts voting with 1 weight each have the same power as a single account voting with 100 weight, since both situations have the same total. | |||
How is this weight of power determined? In most of the original functioning DAOs, power is dictated by ownership of the currency token. In that case plutocracy is the ''de facto'' governmental structure. Little reflection is needed before most new DAO architects reject this design. Instead the common solution is to build their DAOs on reputation. | |||
=== Reputation === | === Reputation === | ||
''Main page: [[Reputation | ''Main page: [[Reputation]]'' | ||
Reputation is a personal judgement based on your past actions. Business relies on your counterparty’s reputation to predict how they will act during a transaction, to give you the confidence to enter a bargain. History has repeatedly proven<ref>Avner Greif (1994) "Cultural Beliefs and the Organization of Society: A Historical and Theoretical Reflection on Collectivist and Individualist Societies", The Journal of Political Economy. 102 (October 5): 912–50. doi:10.1086/261959. S2CID 153431326.</ref> the proper attitude for a healthy market environment is to seek to improve and protect your reputation for the long term, not to simply acquire as much money as possible in a single business deal. A secure and reliable system that accounts for meaningful reputation transforms such zero-sum competitive behavior concerned with immediate profits into an environment which motivates future-oriented, sustainable cooperation. When a single game turns into a repeated game<ref>George J. Mailath & Larry Samuelson (2006) ''Repeated Games and Reputations: Long-Run Relationships'', Oxford University Press.</ref>, the incentives are transformed. In a system with repeated business, reputation is actually a positive sum quality, since it can be created from nowhere. Whenever two parties behave well and collaborate productively, perhaps sacrificing their own short-term gain on some aspects of the deal, they produce valuable reputation that signals the potential for further positive interactions in the future.<ref>Craig Calcaterra & Wulf Kaal (2021) ''Decentralization'', De Gruyter, Chapters 4 and 6.</ref> | |||
How can we foster a culture which respects and values reputation more than money in a DAO which allows pseudonymous members to join or leave at will? Properly designing and programming a robust mechanism that is secure against the infinite strategies for gaming any algorithmic reputation system is not a simple task. DGF is built to capture the meaning of genuine reputation with digital representations, REP tokens. [[Reputation tokenomics]] is devoted to specifying precisely the economic value of a REP token to objectively determine how accurate that representation is. | |||
== Examples == | |||
*[[Block producer DAO|Block production]] - DAO using REP to determine randomized block producer for blockchain consensus. | |||
*[[Stable coin governance|Stable coin]] - DAO devoted to managing the protocols of a decentralized currency minting mechanism. | |||
*[[Arbitration DAO]] - parties may trigger 3rd party [[Judicial governance#Arbitration|arbiter power]] by adding [[Arbitration smart contract|template language]] to any smart contract - allows appeals for any smart contract | |||
*Gig jobs | |||
**[[Software Review DAO]] | |||
*Oracles | |||
**[[Decentralized news media|DeNM]] - Decentralized news media network. | |||
* deFi | |||
**Banking rollup DAO | |||
**[[Underwriting]] | |||
**Marketplaces | |||
***ForEx | |||
***Commodities | |||
***Equities | |||
*** Derivatives | |||
**[[Chit fund]] - A decentralized and global approach to the banking functions of investment, loans, and insurance using a generalization of the traditional chit fund scheme. | |||
*Social collaboration | |||
**[[Science DAO Framework|Science Research Organizations]] | |||
*** Peer to Peer Technology - The decentralized society for research, development, and sharing of P2P tools. | |||
*** Decentralized Governance - The decentralized society for analysis and development of new approaches to the organization and guidance of decentralized networks | |||
** [[Social DAO|Social organizations]] | |||
*** Grants | |||
****[[Scholarship DAO|Scholarships]] | |||
****[[Poverty Relief DAO|Poverty relief]] | |||
*** Community policing | |||
***Social harmony | |||
**[[AI Governance DAO|AI governance]] | |||
==Code== | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[DAO Governance Framework|DGF]] | |||
* [[Governance|DAO Governance]] | |||
** [[Validation Pool]] | |||
** [[Forum]] | |||
*** [[Forum reference mechanisms]] | |||
* [[DAO Governance Framework#DGF workflow|DAO workflow]] | |||
* [[Reputation]] | |||
* [[Reputation tokenomics]] | |||
== Notes & References == | == Notes & References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:14, 5 November 2023
A DAO is a decentralized autonomous organization. A DAO is the fundamental unit of consideration in the DGF project. Commonly, a DAO is a for-profit group run using P2P tools, such as blockchain smart contracts, to automate its governance.
The typical DAO we consider in the DGF project may be thought of as a decentralized, global corporation that uses the internet and computing technology, to make business transactions and to govern itself. As such, a DAO is a community-driven, for-profit cooperative that relies on programming to stay organized.
However, corporations are not the perfect image to conjure when thinking about what a DAO is. In some ways, an open DAO is more like a continual marketplace, where anyone can join or leave at any time. The major difference from a traditional marketplace is that there is no central person or body in charge of a DAO. This type of marketplace is run by the very people who participate in it, with fluid changes in relative power based on participation.
Under DGF, in a for-profit DAO the workers get paid directly after a review period where the other workers have a chance to evaluate whether the work was up to their group standards. The standards are set by the workers directly through DGF governance.
Conceptual overview[edit | edit source]
Decentralized means the opposite of centralized. An ideal centralized organization has a completed pyramidal-hierarchical power structure with a single ruler on top (Figure 1a) which dictates authority, distinguishing those above from those below. Perfect decentralization would be absolutely flat (Figure 1b). Imagine a radical direct democracy, where every decision is made with consensus by the entire membership, without fixed roles of authority.
Figure 1: Centralized vs decentralized – hierarchical vs. flat power
Autonomous means the group governs itself. A DAO is not subject to direct control from outside the group.
A DAO being an organization, means it consists of a coherent collection of members. Coherent means its members cooperate toward a common socio-economic goal. They follow a common set of protocols designed to serve their common values.
The term for the technology that enables decentralized organization is peer-to-peer technology. P2P tech (see Main Article: P2P technology) consists primarily of the internet, zero-knowledge proofs (including public-key digital signatures), hash functions (a universal tool for organizing data and error-correcting), and the software architecture of blockchains and distributed hash tables.
DGF can be applied to build any type of DAO, but the primary concern of the DGF project is to create the governance structure for the most difficult type to build—a profit-centered, open-source, democratically-governed network which is open to pseudonymous, international members—primary DAOs.
Primary DAOs[edit | edit source]
The following qualities maximize the effectiveness of a DAO. A DAO which embodies these ideal qualities is called a primary DAO. In the context of DAO building, let us carefully explain and justify all these terms:
1. Openness
2. Pseudonymity
3. Transparency
4. Open Source
5. Security
6. Weighted Democracy
7. Reputation Incentive
Before defining these terms, it is crucial to recognize they are ideals. As such they are never expressed with perfect purity in real world organizations. Actual DAOs exist on a spectrum of these qualities.
Openness[edit | edit source]
A DAO being open means its rules for accepting new membership is unrestrictive—everyone in the world has equal access to join, an equal opportunity to gain power, and an equal freedom to leave (while taking much of their personally accumulated value with them).[1] It is preferable that a DAO adopt these properties of openness for two primary reasons.
First, an open network encourages greater growth. Combined with the network effect, this means a decentralized group grows in power faster than a centralized organization as its membership increases if communication is effective. To understand the network effect, notice how members don’t merely have connections, they have individual connections. Connections grow quadratically with membership. A group of members also has an exponential number of potential subgroups. Each subgroup of size has different role assignments. Etc. As a group grows, there is more talent and more knowledge with quadratically more connections and exponentially more arrangements to foster more powerful collaboration. A decentralized organization with effective communication leverages the available energy of its members more effectively than a centralized organization.[2] An open DAO leverages the available energy of the entire population more effectively than a closed DAO. This network effect is a major reason that decentralized organizations can be superior to centralized organizations, because a rigid hierarchy is limited to a single power structure for organizing its members to achieve all the tasks it will ever perform. When the market changes, a centralized system is not as agile as a decentralized system for solving new problems.
The second major reason openness is ideal is that it serves the social good. It is a matter of basic justice that all people in a society are given equal opportunity to participate in all of its institutions. People prefer not to participate in a group that does not serve their values, especially one that limits their opportunities to gain power in the group. More importantly, they should not be forced to participate.
However, openness is a major security risk that needs to be continually addressed. Equal opportunity to participate is essential, but the types of participation that are beneficial to the group are naturally limited. Members who behave poorly must lose some of their power in the group, lest the group be destroyed by selfish behavior which virally spreads until the group becomes completely disorganized. Corruption must be limited or it will multiply until it destroys the group. Therefore, to maintain openness, a DAO needs strong, automated, executive governance.
Pseudonymity[edit | edit source]
Pseudonymity means a member may participate with one or more fabricated[3] identities. An example is when you invent a fake username on an internet message board. It is preferable that a DAO allow members to join pseudonymously for three major reasons.
First, privacy is essential for protecting the individual. Since all transactions must be openly monitored by anyone in the decentralized network, every behavior in the DAO is recorded eternally and broadcast globally. In addition to the fear of social censure decades after any particular behavior, keeping a record of a citizen’s minute behaviors is a powerful tool which encourages governmental repression of its citizens at all levels. Pseudonymity is the closest one can achieve to anonymity on a transparent platform that remembers transactions and gives its members power and rewards.
Second, this protection of individuals’ privacy encourages more members to join. Again, the network effect gives larger groups more than a quadratic advantage in the many sub-dimensions of power, capital, and knowledge.
Finally, pseudonymity encourages a culture of forgiveness. Mistakes are inevitable. Forgiveness is essential to promote the network effect. Regardless of the intention behind the mistake, if it is possible to forgive members without eroding group cohesion, a culture supporting redemption should be promoted. Though it should be recognized that, unfortunately, pseudonymity makes apologies unnecessary, since they can simply quit and start fresh with a new identity. Conscious of this fact, a culture of redemption can still be encouraged if the DAO sets up protocols giving greater power to someone who has atoned for a mistake than to new members.
However, pseudonymity is a major security threat in an open DAO as it opens the group to sock puppet attacks, which we discuss below.
Transparency[edit | edit source]
Transparency means the functions of the DAO are publicly observable. In particular, the types of technology used, the specifications for the design of the technology, the membership, the actual rate and quantity of computations or transactions, the protocols for acceptable transactions, protocols for policing transactions, the protocols for changing protocols, and even the culture of decision making, can all be made more or less transparent in any network. Inasmuch as knowledge is limited to certain individuals, when transparency is limited in any way, power becomes centralized among the subpopulation of the DAO which has the knowledge. Thus transparency is correlated with openness and power decentralization in DAOs. However, transparency is a major threat to members’ privacy, which is ameliorated when the DAO supports pseudonymity.
Open source[edit | edit source]
Open source means, minimally, that the computer code that runs the technology the DAO uses is publicly available knowledge. Similar to transparency, open-source protocols are generally necessary in an open DAO because inasmuch as it is decentralized, all members are more or less equal. No member has privileged information. Without a more powerful leader, everyone in the network needs to be able to monitor everyone else. Everyone needs to have access to the knowledge of the architecture of the system in order to audit its functioning. This is not strictly necessary in a weighted democratic governance system, since certain members can have greater power than others. But inasmuch as such power disparities obtain, the DAO is less decentralized.
Maximal open-source tech means the legal right to use that technology is given away freely, without claiming any royalties, to anyone else who wishes to use it, for any reason. An example is the Apache license[4], which governs a significant portion of internet technology. The Apache license allows you to adapt their free tech and improve it. Moreover, you can then claim ownership of your improvements and demand royalties. Such maximal open-source protocols are not necessary for any DAO to adopt. However, it is good practice to assume your protocols will be maximally open source when designing a DAO, because the international character of any open DAO makes jurisdictional questions impractical to decide and enforce. Protecting your IP in this environment is better handled by using the first mover advantage, combined with the network effects that make your DAO more powerful than any later imitators. This works best when additionally, a culture of proper referencing evolves to acknowledge and fairly reward improvements from the past. Such meritocracy can promote a more effective collaboration environment than one which stresses competition and secrecy.
Security[edit | edit source]
Security is a constant concern in the design of an open-source protocol. Especially when the network is open to pseudonymous members. Byzantine behavior in a decentralized network, is defined as actions which violate the majority agreed protocols. When there is no dictator ruling your platform, and you accept asynchronous distributed transactions entering from any node, it is impossible to achieve perfect intelligence about the state of the network, since Byzantine nodes can pass false messages in the gossip network. There are several theorems in computer science that govern what is possible when designing a protocol for distributing digital token rewards in a DAO. A famous example is the 66% non-Byzantine limit for the pBFT algorithm. In general, no decentralized system can survive forever in the face of 51% Byzantine actors. Therefore some restrictions to openness are necessary.
Another major security risk to a decentralized platform is a sock puppet attack. Sock puppets are multiple pseudonymous accounts that a single member creates and controls with separate passwords to hold digital tokens. The purpose of sock puppet accounts is to trick the network into believing the different pseudonymous identities represent multiple people. This eliminates any chance that a DAO without KYC protocols can achieve honest governance under simple one-person-one-vote democracy. Since anyone on the planet has equal opportunity to participate under a fabricated identity, a single actor can create countless sock puppet accounts to overwhelm the voices of honest members. Therefore, any DAO work model or governance design must account for this eventuality. The solution to fighting sock puppet attacks, is a weighted democracy which assign rewards and power based on carefully audited measures of positive contributions to the group.
Weighted Democracy[edit | edit source]
A weighted democracy is a governance structure where the power to decide the protocols for the DAO is determined by vote (democracy), but the power of each person’s vote may be different (weighted).
Democracy of some type is necessary to achieve decentralized organization because inasmuch as control is not distributed amongst the members widely, then the group is less decentralized. Decentralization can be more effective than centralization, when effectively utilized, for three main reasons: 1. power is given to the most appropriate servant, 2. information at the edge is revealed, 3. the processing power of the entire group is utilized (with enough eyes, every problem is shallow).
The weighting of the democracy is necessary in an open pseudonymous group, because it eliminates the threat of sock puppet attacks: 100 sock puppet accounts voting with 1 weight each have the same power as a single account voting with 100 weight, since both situations have the same total.
How is this weight of power determined? In most of the original functioning DAOs, power is dictated by ownership of the currency token. In that case plutocracy is the de facto governmental structure. Little reflection is needed before most new DAO architects reject this design. Instead the common solution is to build their DAOs on reputation.
Reputation[edit | edit source]
Main page: Reputation
Reputation is a personal judgement based on your past actions. Business relies on your counterparty’s reputation to predict how they will act during a transaction, to give you the confidence to enter a bargain. History has repeatedly proven[5] the proper attitude for a healthy market environment is to seek to improve and protect your reputation for the long term, not to simply acquire as much money as possible in a single business deal. A secure and reliable system that accounts for meaningful reputation transforms such zero-sum competitive behavior concerned with immediate profits into an environment which motivates future-oriented, sustainable cooperation. When a single game turns into a repeated game[6], the incentives are transformed. In a system with repeated business, reputation is actually a positive sum quality, since it can be created from nowhere. Whenever two parties behave well and collaborate productively, perhaps sacrificing their own short-term gain on some aspects of the deal, they produce valuable reputation that signals the potential for further positive interactions in the future.[7]
How can we foster a culture which respects and values reputation more than money in a DAO which allows pseudonymous members to join or leave at will? Properly designing and programming a robust mechanism that is secure against the infinite strategies for gaming any algorithmic reputation system is not a simple task. DGF is built to capture the meaning of genuine reputation with digital representations, REP tokens. Reputation tokenomics is devoted to specifying precisely the economic value of a REP token to objectively determine how accurate that representation is.
Examples[edit | edit source]
- Block production - DAO using REP to determine randomized block producer for blockchain consensus.
- Stable coin - DAO devoted to managing the protocols of a decentralized currency minting mechanism.
- Arbitration DAO - parties may trigger 3rd party arbiter power by adding template language to any smart contract - allows appeals for any smart contract
- Gig jobs
- Oracles
- DeNM - Decentralized news media network.
- deFi
- Banking rollup DAO
- Underwriting
- Marketplaces
- ForEx
- Commodities
- Equities
- Derivatives
- Chit fund - A decentralized and global approach to the banking functions of investment, loans, and insurance using a generalization of the traditional chit fund scheme.
- Social collaboration
- Science Research Organizations
- Peer to Peer Technology - The decentralized society for research, development, and sharing of P2P tools.
- Decentralized Governance - The decentralized society for analysis and development of new approaches to the organization and guidance of decentralized networks
- Social organizations
- Grants
- Community policing
- Social harmony
- AI governance
- Science Research Organizations
Code[edit | edit source]
See Also[edit | edit source]
Notes & References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Open is synonymous with permissionless in public blockchains.
- ↑ One of the major reasons centralized groups have been more competitive against decentralized groups in the past is that the tree structure of a hierarchy is the most efficient means of communication. It eliminates all redundancy. With contemporary information technology, however, we can now communicate practically with maximum redundancy. Everyone in a group of practically any scale can broadcast to and monitor the entire group.
- ↑ Pseudonym technically means false identity, which has a negative connotation. It would be preferable to have a more neutral term meaning fabricated name, such as technonym, synthenym, artinomen, or fabrinomen, since the identities we are discussing are not necessarily inherently false. However, the term pseudonym is firmly established in the field.
- ↑ https://www.apache.org/licenses/ Retrieved 18/2/2023
- ↑ Avner Greif (1994) "Cultural Beliefs and the Organization of Society: A Historical and Theoretical Reflection on Collectivist and Individualist Societies", The Journal of Political Economy. 102 (October 5): 912–50. doi:10.1086/261959. S2CID 153431326.
- ↑ George J. Mailath & Larry Samuelson (2006) Repeated Games and Reputations: Long-Run Relationships, Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Craig Calcaterra & Wulf Kaal (2021) Decentralization, De Gruyter, Chapters 4 and 6.