Block producer DAO
DGF is used to make Block producer DAOs (BpDAOs) which govern block production in blockchains. These BpDAOs consist of members who earn REP tokens for producing canonical blocks and governing the development of the system. The REP minting mechanism of DGF incentivizes faithful production of blocks with a consensus mechanism called Proof of Reputation (PoR). DAO governance guides and rewards improvements to the platform.
Overview
A fork of Ethereum (or any other blockchain) with the original consensus mechanism initiates the new blockchain. The difference between an original blockchain consensus mechanism and a DGF variation is in governance. The fees are in the native currency token denoted $. Initially $ is ETH in the case of an Ethereum fork. Then REP is minted when a block is produced. Distribution of REP and $ fees follow DGF flow:
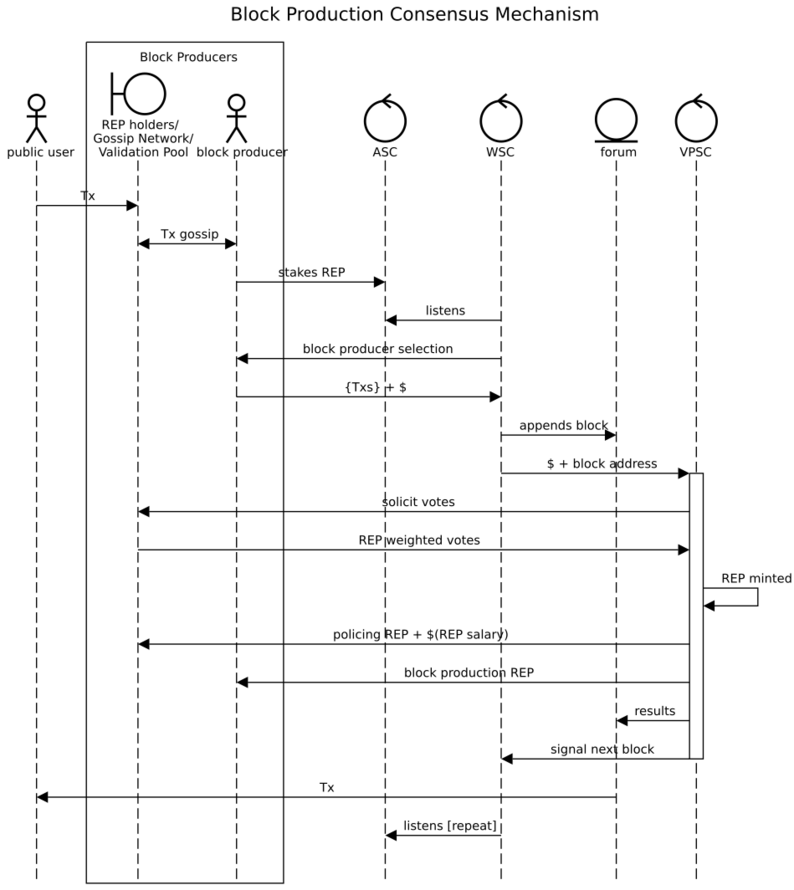
- A block producer is a holder of REP. A producer signals their availability to produce blocks by encumbering their REP in the availability smart contract (ASC).
- Previous blocks pseudorandomly select a producer from the active ASCs.
- The selected producer follows the current protocol for block production which is encoded in the current work smart contract (WSC).
- When the block is finished it is posted to the Forum with the $ fees collected from the block, opening a Validation Pool (VPSC):
- The fees include any transaction fees and any production taxes--meaning newly minted $ from that block.
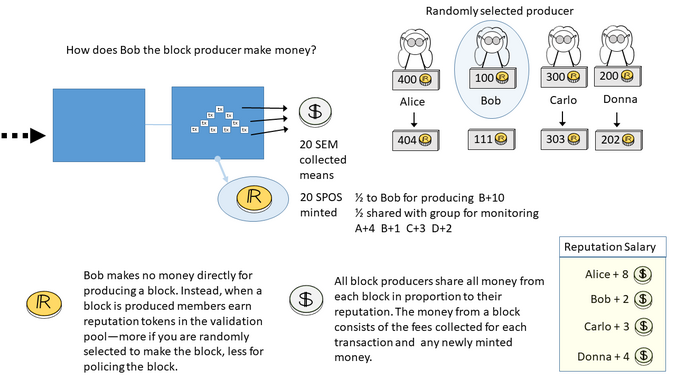
- The VPSC mints new REP in proportion to the $ fees and encumbers the REP appropriately--default is 50% for the producer, 50% against the producer.
- The Bench of experts evaluate the block and stake their REP on the outcome.
- VPSC resolves the vote, distributing the REP to the winners in proportion to their stakes.
- VPSC distributes the $ fees to all members of the DAO in proportion to their REP holdings (REP salary).
- Repeat
Comments
Governance
Executive
The entire high-level algorithm described above is automated as part of executive governance. Each vote in each validation pool is an explicit coordination action between the set of all nodes maintaining the blockchain. However, these votes are automated.
If the node's client software recognizes a block as being properly constructed (lines 53/54), then the client votes to validate. If not, the client votes to reject. If a block is invalidated, the REP encumbered by the block producer in the ASC is slashed. This has the effect of motivating block producers to run the client software unhacked.
Participation in policing is naturally incentivized by the Validation Pool, which rewards participants with half of all newly minted REP. This also stabilizes the owership of REP as new REP does not all go to the lucky producer who was selected to produce the new block.
Legislative
The above description of the algorithm does not include the important aspect of legislative governance. Continual improvements to the algorithm and software are incentivized since the WSC will include references to fund governance proposals that update the WSC, itself, and any other hard protocols that are improved. As detailed in the legislative governance page, such proposals involve slow and conscious deliberation and voting between members, unlike the automated executive governance of the client software for active block production.
Judicial
Judicial governance under DGF makes it possible to retroactively slash REP that was used to violate the values of the Block Producer DAO. This allows the group to implement governance to prevent spirit-of-the-law-violations, such as censorship. Censorship in block production means, for example that a block producer chooses not to include a transaction in a block. Reasons for censorship include arbitrage opportunities such as leaving out votes in the validation pool so those producers don't share in the rewards for policing, manipulating the pseudorandom selection algorithm by leaving out ASCs, and leaving out customers' transactions to arbitrage markets.
Scaling
Governance under DGF allows nimble reweighting of parameters in the WSC to adjust to network performance. For example, when the number of block producers grows to make validation pool coordination cumbersome, random selections of subpopulations of the block producers can be made each round to optimize for security, latency, throughput, and bandwidth.
Variations
There are many improvements possible on every aspect of the basic outline given above. DGF provides an evolutionary structure with incentives to continually improve the system. This is necessary for any PoS consensus mechanism, given the inevitable threat of gaming any cooperative system leads to an arms race of attack and defense as the system becomes more successful and valuable.
In this section we give an introduction to areas that will be continually improved.
Availability Smart Contract
Pseudonymous REP tied together without KYC
One important aspect of this implementation of DGF is that a block producer's REP can be tied together without exposing the owner of the wallet holding the REP. The REP used to run the automated block production client software grows automatically as they participate in block production and policing. The REP encumbered in the ASC can be tied to the REP gained by minting blocks when their ASC is selected. If it is ever necessary to slash a block producer's REP, then all of the REP they've used can be slashed without revealing the block producer's identity.
More stable selection
Improvements to the automated selection process can be made to select REP in a more equitable manner. The lottery process of selecting members according to power, statistically will maintain power ratios if all members are continually encumbering all their REP in ASCs. Larger wallets of REP will always remain larger if the owner continually runs the block production software, and the effect is linear (stochastic process argument). However, we can incentivize homogeneity between wallets if we implement a more complicated selection process of remembering which REP was selected: REP that has been selected for block production is not selected again until the entire list of active ASCs are selected. This encourages sock puppets, but that effect is mollified by tying together REP as in the previous subsection.
Block Producer selection
At Step 2 in the above process, the block producer is pseudo-randomly selected from the active Availability Smart Contracts. If this is not done carefully, a Byzantine actor who is the latest active block producer can anticipate the pseudo-randomness and manipulate the algorithm so that he is selected again, in perpetuity, which would destroy the decentralization of the blockchain.
To guarantee the pseudo-random selection mechanism is resistant to such capture, there are several algorithms available. Here we describe a basic Commit-Reveal scheme, such as the Randao algorithm. Basically, selection of the block producer is done in two stages. First, every block producer sends an encrypted salt message for the pseudorandom algorithm to the current block producer to include in the current block. Then after the block is published, the block producers send in their keys to unencrypt their salt messages in the next block. The union of the salts is added to the pseudorandom number generator to determine the next block producer.
This creates complications for reasoning about what to do when the network is fragmented and some members fail to participate, or when a block producer censors commits or reveals. However, such attacks can be policed and disincentivized with judicial governance.
Work Smart Contract evolution
Validation protocols
Censorship resistance
Code
Sequence diagrams
The following sequence diagrams illustrate the basic algorithm for block production. The first diagram illustrates basic DGF flow: applied to block production.
The second diagram illustrates the reference mechanism, which provides a means of bootstrapping governance by making proposals which cite older proposals. This gives an incentive mechanism for a community to organically evolve its protocols
Pseudocode
Block Production Algorithm
Inputs: dynamic set of desired transactions from customers
Output: a blockchain of settled transactions
__________
Definitions
REP := reputation token
$ := currency token
wallet := program for holding tokens for an individual participant
Tx := transaction sending a currency token from one wallet to another
customer := has
* unique identifying address
* wallet for holding $ and sending Txs
block producer := has
* unique identifying address
* wallet for receiving $ and REP
* ability to give inputs to ASC, WSC, & VPSC
ASC := Availability Smart Contract
WSC := Work Smart Contract
VPSC := Validation Pool Smart Contract
Forum := database holding history of blocks & Validation Pool results
gossip network := set of all active Tx held by block producers
Validation Pool := dynamically changing set of block producers who are currently policing a proposed block
__________
Algorithm
For i = 1 to infinity
Produce block i := {
WSC function:= {
* listens to active ASCs
* pseudorandomly selects 1 block producer based on weights of encumbered REP in ASCs
* announces current block producer
* takes current block producer's REP from ASC
* waits for a set of Txs from current block producer
* produces a block
* publishes proposed block to Forum
* sends 4 things to the VPSC:
1. $ from Txs
2. new $ minted in block
3. block producer's REP from ASC
4. address of proposed block
}
VPSC function: := {
* mints REP tokens in proportion to $ tokens
* announces new validation pool and proposed block address to block producers
* collects votes from block producers
* tallies votes to determine distribution of new REP tokens
* distributes new REP
* distributes REP salary
* publishes vote results to Forum
[Forum signals to Tx status to customer]
* signals WSC to produce next block
}
}