Decentralized underwriting
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
??Insurance DAOs (iDAOs) for creating decentralized underwriting markets, based on this paper.[1]
Insurance DAO protocols
Components
- DAO = {Underwriters}
- Underwriter ∋ REP tokens a) Propose contracts with REP b) Police contracts with REP
- Insurance contract (Work smart contract)
- Validation Pool
Token scheme
Workflow
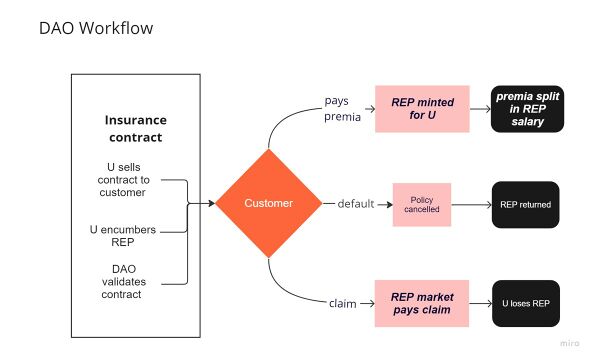
(See Figure 1.)
- Underwriter sells a contract to a customer.
- encumbers the canonical amount of REP in the contract.
- Contract Validated by DAO.
- Customer a) pays premia, or b) defaults, or c) claims
- DAO a) mints REP for proportional to premia & distributes REP salary, or b) cancels contract, or c) pays claim by selling encumbered REP at market
Consequences
Properties engendered
- More auditable/transparent
- More stable, trustworthy
- More meritocratic (rewards and punishment are isolated to the agent)
- Democratized access to participation at all levels
Tokenomics
Capital reserves can be eliminated
economic justification
Where we stand practically in deFi
Missing:
- (d) oracles
- *adjudication
- (d/e) stable coin
- (e) smart contracts
- regulatory clarity
Code
See Also
Notes & References
- ↑ Craig Calcaterra, Wulf A. Kaal, & Vadhindran K. Rao, (2019) "Decentralized Underwriting". Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3396542 (Retrieved 2023 March 16)