Uniswap
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
How it works?
Overview
Uniswap is an automated liquidity protocol powered by a constant product formula and implemented in a system of non-upgradeable smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.[1]
Timeline
Version Evolution
| V1 | V2 | V3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | Vyper: ETH20-ETH | NA | NA |
| V2 | Solidity: ETH20-ETH20 | NA | |
| V3 | Ethereum and Optimism | Concentrated Liquidty, Active Liquidity, Range Limit Orders.
|
Concepts
Liquidity Pools
Swaps
Constant Product Formula
x * y = k
Concentrated Liquidity (CL)
As long as the pairing of ETH and DAI stay within a range ($1500-2500), User Red who invested much less than User Blue ($1200 vs. $10,000) can still earn the same trading fees (see Figure CL).
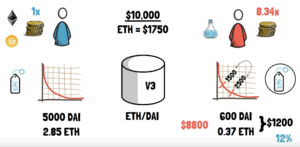
Figure CL: An example of how Uniswap V3's concentrated liquidity concept works.[2]
Active Liquidity
Range Limit Orders
Questions
- How does the relate to DGF?
- Can it help with validation pool REP management and redistribution? [Context: Odra Collaboration]
- REP and cryptocurrencies are fundamentally different. REP is meant to be a low velocity asset that has non-fungible qualities.
- Can it help with validation pool REP management and redistribution? [Context: Odra Collaboration]
References
- ↑ Protocol Overview: How Uniswap works. (n.d.). Uniswap. Retrieved November 8, 2023, from https://docs.uniswap.org/contracts/v2/concepts/protocol-overview/how-uniswap-works
- ↑ UNISWAP V3 - New Era Of AMMs? Architecture Explained. (2021, March 23). Finematics. Retrieved November 8, 2023, from https://finematics.com/uniswap-v3-explained/