Chit Fund DAO: Difference between revisions
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== Background == | == Background == | ||
A [[wikipedia:Chit_fund|chit fund]] is a folk banking scheme traditionally used by people without access to formal banking institutions. The term ''chit fund'' comes from India, where it | A [[wikipedia:Chit_fund|chit fund]] is a folk banking scheme, traditionally used by people without access to formal banking institutions. The term ''chit fund'' comes from India, where it has been used by a significant percentage of the population for many years, and is legally regulated in many regions. Similar [[wikipedia:Rotating_savings_and_credit_association|decentralized savings and credit schemes]] are used throughout the world to replicate the functions of banking, especially where people do not have access to centralized banking institutions. | ||
Banking involves two money processes: deposits and withdrawals. The sequence determines the type of banking. Consider for instance, the fundamental banking practices of loans, investments, and insurance. A ''loan'' is an initial withdrawal of money followed by a series of deposits. An ''investment'' is a series of deposits, followed by a withdrawal. ''Insurance'' is a series of deposits, with a withdrawal at random times between the deposits. These three types of banking are unified by the scheme in a basic chit fund, as illustrated next. | Banking involves two money processes: deposits and withdrawals. The specific sequence determines the type of banking. Consider, for instance, the fundamental banking practices of loans, investments, and insurance. A ''loan'' is an initial withdrawal of money followed by a series of deposits. An ''investment'' is a series of deposits, followed by a withdrawal. ''Insurance'' is a series of deposits, with a withdrawal at random times between the deposits. These three types of banking are unified by the scheme in a basic chit fund, as illustrated next. | ||
=== Basic chit fund scheme === | === Basic chit fund scheme === | ||
In a traditional chit fund there are several subscribers and an organizer. As a basic example, suppose | In a traditional chit fund there are several subscribers and an organizer. As a basic example, suppose 50 subscribers agree to deposit $200 (the premium) in the fund every month for 50 months. Each month an auction takes place, where the subscribers can bid to receive a fraction of the current total chit fund. The lowest bid gets to keep the amount they bid. Any remaining money is held over for the next month's auction. Once you win an auction, you can’t win another, but you are still required to add your $200 each month until the end. So the number of subscribers is always equal to the number of months the chit fund runs in traditional chit funds (though this stipulation is removed in the generalized cfDAO). | ||
In this example, notice that $ | In this example, notice that $10,000 is added to the fund each month for 50 months (<math>$200\times 50</math> members, unless someone defaults). For $200 entry you can withdraw almost $10,000 in the first months, if you bid lowest. Early winning bids will typically be from people eager to use the chit fund as a loan, so they will typically be lower than $10,000. Since the excess money remains in the fund for later bids, the fund typically grows, in which case it holds more than $10,000 later. Therefore, early withdrawal is analogous to taking a bank loan that is repaid for 50 months with interest. Later withdrawal is similar to a bank deposit that earns interest. Others can use the fund as insurance by withdrawing when they need it at any time between the beginning and the end. | ||
However, the core difficulty in implementing any chit fund is organizing it. The primary threat is that a subscriber will win an early bid, then fail to make the rest of the deposits--defaulting. Traditional chit fund organizers make a 5% commission, for the primary goal of ensuring subscribers do not default. This is especially challenging in a decentralized, open, global financial scheme. How can we guarantee the default rate is low enough to justify participation from pseudonymous participants? To solve this problem, the chit fund needs to be insured against the risk. Therefore, the subscribers of the cfDAO require underwriting. | |||
However, the core difficulty in implementing any chit fund is organizing it. The primary threat is that a subscriber will win an early bid, then fail to make the rest of the deposits--defaulting. Traditional chit fund | |||
== Basic cfDAO function == | == Basic cfDAO function == | ||
| Line 35: | Line 21: | ||
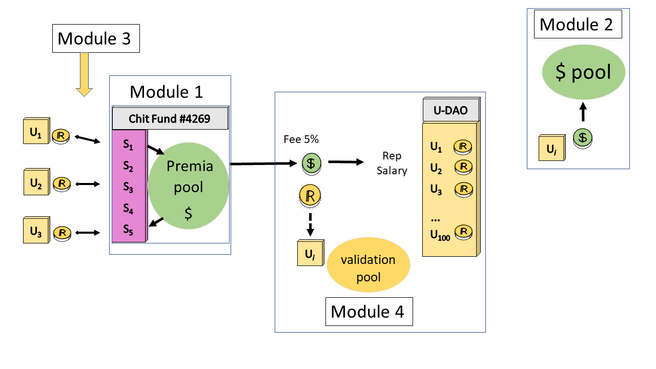
In the above figure, we illustrate five basic interoperating smart contracts which govern the cfDAO. | In the above figure, we illustrate five basic interoperating smart contracts which govern the cfDAO. | ||
In the first module, the chit fund smart contract (cfSC) governs instantiations of the chit fund. Each subscriber <math>S_i</math> makes monthly deposits, called premia, into the chit fund. This gives subscribers the right to bid on the | In the first module, the chit fund smart contract (cfSC) governs instantiations of the chit fund. Each subscriber <math>S_i</math> makes monthly deposits, called premia, into the chit fund. This gives subscribers the right to bid on the fund--which is the ''premia pool''. The cfSC keeps the accounting for each round until the chit fund's conclusion. | ||
The second module is the Reserve Smart Contract (rSC), which initiates the underwriting reserve. In this smart contract, underwriters pool money to be held in reserve. This reserve money is used to guarantee chit funds continue to be funded properly in case any subscriber defaults. Each underwriter who deposits cash in the rSC is issued proportional underwriting REP tokens (uREP). | The second module is the Reserve Smart Contract (rSC), which initiates the underwriting reserve. In this smart contract, underwriters pool money to be held in reserve. This reserve money is used to guarantee chit funds continue to be funded properly in case any subscriber defaults. Each underwriter who deposits cash in the rSC is issued proportional underwriting REP tokens (uREP) which lay claim on the portion of the cash reserve. | ||
In the third module, underwriters may encumber uREP tokens in order to underwrite chit fund subscribers accepted by the underwriter. In case a chit fund subscriber defaults, then this Underwriting Smart Contract (uSC) will use the uREP tokens to continue the deposits until the chit fund ends. For this service a chit fund subscriber must pay an underwriter a fee. For example, a standard | In the third module, underwriters may encumber uREP tokens in order to underwrite chit fund subscribers accepted by the underwriter. In case a chit fund subscriber defaults, then this Underwriting Smart Contract (uSC) will use the uREP tokens to continue the deposits until the chit fund ends. For this service, a chit fund subscriber must pay an underwriter a fee. For example, a standard organizer's fee in a traditional chit fund is 5%. | ||
In the fourth module, the underwriter DAO follows basic [[DAO Governance Framework#DGF workflow|DGF workflow]]. Instead of keeping the underwriting fee, the underwriter is given uREP, and the fee is distributed to all uDAO members in proportion to their uREP holdings through the [[Reputation#REP Salary Mechanism|REP salary]]. The uDAO allows the members to police each instantiation of the chit fund through the [[Validation Pool]], to guarantee all subscribers are fully underwritten to ensure successful conclusions. Chit funds which are not fully underwritten are automatically rejected. | In the fourth module, the underwriter DAO follows basic [[DAO Governance Framework#DGF workflow|DGF workflow]]. Instead of keeping the underwriting fee, the underwriter is given uREP, and the fee is distributed to all uDAO members in proportion to their uREP holdings through the [[Reputation#REP Salary Mechanism|REP salary]]. The uDAO allows the members to police each instantiation of the chit fund through the [[Validation Pool]], to guarantee all subscribers are fully underwritten to ensure successful conclusions. Chit funds which are not fully underwritten are automatically rejected. | ||
| Line 59: | Line 45: | ||
For example, if everyone is going to save money the entire time, it's better to get out of the chit fund if you are planning on investing, in order to join another fund that has members who ''are'' seeking loan opportunities. So you should always bid <math>$Np</math> on the first round and get out if no one bids low. | For example, if everyone is going to save money the entire time, it's better to get out of the chit fund if you are planning on investing, in order to join another fund that has members who ''are'' seeking loan opportunities. So you should always bid <math>$Np</math> on the first round and get out if no one bids low. | ||
=== Web3 improvements === | |||
Web3 technology can greatly improve the efficiency and security of the traditional chit fund scheme. | |||
First, a smart contract replaces the organizer, eliminating the risk that the organizer can abscond with the fund. Further, the decreased overhead from automation should typically reduce the 5% organizer commission. | |||
Second, by implementing a subscriber reputational system, honest participation can be tracked across many different chit funds, as people will earn reputation each time they pay their required monthly fee, and lose reputation if they default. The more often they participate honestly, the larger their reputation will grow. Then participation in larger and more complex chit funds can be dependent on reputation, which will incentivize healthy collaboration. | |||
One major source of overhead that makes this subscriber reputation scheme less efficient, is the inevitable possibility of subscribers defaulting on paying the premia. It’s been estimated that 35% of chit fund subscribers have defaulted at least once recently and 24% have defaulted after winning an auction. If a subscriber defaults, their underwriter suffers. If the system which gives subscribers reputation becomes the major reason an underwriter supports their subscribers, then the system will eventually punish underwriters randomly. Because a market for subscriber REP tokens will eventually emerge, and then people will use the tokens to default and make better profit than can be made participating honestly. This suggests that there will always be a need for the current legacy system of KYC rules and legal rules preventing insurance fraud. However, these rules are at the level of the subscriber-underwriter relationship. Not on the level of the DAO, which is supranational. | |||
The advantage of a supranational DAO is that it enhances the core value proposition of banking and insurance--distributing risk across a deep and diverse market. A supranational DAO has a larger, and therefore more stable, capital reserve of equity tokens (underwriter REP) which are measurably valuable according to the market. This decreases the need for cash reserves, making the system more efficient. | |||
If the default risk can be managed at scale, then another advantage is that larger groups dilute the risk of individual default. A chit fund with a large number of people with high reputation can pay smaller premia for insurance. One million people investing $1 daily for 50 years allows 50 people per day to immediately begin taking an average payout of roughly $20,000. More investors investing smaller amounts in shorter increments, means more people can withdraw at any point. By monitoring and analyzing the performance of a fund, programs can suggest values that can be withdrawn at any given time. By automatically bidding when the fund rises above expected levels (as described in the previous section), the fund can be stabilized to give predictable returns. This prediction become more accurate if multiple funds are connected. | |||
With no initial reserve backing, this allows people to bootstrap their way to greater financial security and stability, assuming the reputation system is sufficiently strong to guarantee a low percentage of defaults. | |||
Like other overhead costs (the appeals process, policing, etc.), insurance is cheaper when the system is running well. The more automated the decentralized economy becomes (thanks to smart contracts and optimized UIs, for instance) the less costly insurance is. The purpose of insurance is to decentralize risk. The new tools of information technology and architectures of P2P distributed computing create more effectively decentralized organizations. Decentralizing risk makes insurance more stable and efficient, which improves the function of the economy. | |||
==Code== | |||
==See Also== | |||
*[[Decentralized underwriting]] | |||
*[[BOND tokens|BONDs]] | |||
*[[Graceful Exit BOND market]] | |||
==Notes & References== | |||
Latest revision as of 11:24, 15 April 2024
The Chit Fund DAO (cfDAO) is a DAO devoted to decentralized banking. The cfDAO generalizes the function of traditional chit funds to make an open global deFi platform for all types of banking. The cfDAO uses DGF to manage its underwriting and governance.
Background[edit | edit source]
A chit fund is a folk banking scheme, traditionally used by people without access to formal banking institutions. The term chit fund comes from India, where it has been used by a significant percentage of the population for many years, and is legally regulated in many regions. Similar decentralized savings and credit schemes are used throughout the world to replicate the functions of banking, especially where people do not have access to centralized banking institutions.
Banking involves two money processes: deposits and withdrawals. The specific sequence determines the type of banking. Consider, for instance, the fundamental banking practices of loans, investments, and insurance. A loan is an initial withdrawal of money followed by a series of deposits. An investment is a series of deposits, followed by a withdrawal. Insurance is a series of deposits, with a withdrawal at random times between the deposits. These three types of banking are unified by the scheme in a basic chit fund, as illustrated next.
Basic chit fund scheme[edit | edit source]
In a traditional chit fund there are several subscribers and an organizer. As a basic example, suppose 50 subscribers agree to deposit $200 (the premium) in the fund every month for 50 months. Each month an auction takes place, where the subscribers can bid to receive a fraction of the current total chit fund. The lowest bid gets to keep the amount they bid. Any remaining money is held over for the next month's auction. Once you win an auction, you can’t win another, but you are still required to add your $200 each month until the end. So the number of subscribers is always equal to the number of months the chit fund runs in traditional chit funds (though this stipulation is removed in the generalized cfDAO).
In this example, notice that $10,000 is added to the fund each month for 50 months ( members, unless someone defaults). For $200 entry you can withdraw almost $10,000 in the first months, if you bid lowest. Early winning bids will typically be from people eager to use the chit fund as a loan, so they will typically be lower than $10,000. Since the excess money remains in the fund for later bids, the fund typically grows, in which case it holds more than $10,000 later. Therefore, early withdrawal is analogous to taking a bank loan that is repaid for 50 months with interest. Later withdrawal is similar to a bank deposit that earns interest. Others can use the fund as insurance by withdrawing when they need it at any time between the beginning and the end.
However, the core difficulty in implementing any chit fund is organizing it. The primary threat is that a subscriber will win an early bid, then fail to make the rest of the deposits--defaulting. Traditional chit fund organizers make a 5% commission, for the primary goal of ensuring subscribers do not default. This is especially challenging in a decentralized, open, global financial scheme. How can we guarantee the default rate is low enough to justify participation from pseudonymous participants? To solve this problem, the chit fund needs to be insured against the risk. Therefore, the subscribers of the cfDAO require underwriting.
Basic cfDAO function[edit | edit source]
The cfDAO relies on an underwriting DAO (uDAO).
In the above figure, we illustrate five basic interoperating smart contracts which govern the cfDAO.
In the first module, the chit fund smart contract (cfSC) governs instantiations of the chit fund. Each subscriber makes monthly deposits, called premia, into the chit fund. This gives subscribers the right to bid on the fund--which is the premia pool. The cfSC keeps the accounting for each round until the chit fund's conclusion.
The second module is the Reserve Smart Contract (rSC), which initiates the underwriting reserve. In this smart contract, underwriters pool money to be held in reserve. This reserve money is used to guarantee chit funds continue to be funded properly in case any subscriber defaults. Each underwriter who deposits cash in the rSC is issued proportional underwriting REP tokens (uREP) which lay claim on the portion of the cash reserve.
In the third module, underwriters may encumber uREP tokens in order to underwrite chit fund subscribers accepted by the underwriter. In case a chit fund subscriber defaults, then this Underwriting Smart Contract (uSC) will use the uREP tokens to continue the deposits until the chit fund ends. For this service, a chit fund subscriber must pay an underwriter a fee. For example, a standard organizer's fee in a traditional chit fund is 5%.
In the fourth module, the underwriter DAO follows basic DGF workflow. Instead of keeping the underwriting fee, the underwriter is given uREP, and the fee is distributed to all uDAO members in proportion to their uREP holdings through the REP salary. The uDAO allows the members to police each instantiation of the chit fund through the Validation Pool, to guarantee all subscribers are fully underwritten to ensure successful conclusions. Chit funds which are not fully underwritten are automatically rejected.
Initially the rSC requires underwriters to make 100% capital reserves. However, as detailed in the page on decentralized underwriting, this 100% reserve requirement can be safely diminished once stable fees are proven, because the uREP tokens will gain intrinsic value from the REP salary. A fifth module makes this explicit, with a uREP Marketplace Smart Contract. When a subscriber defaults, the uREP tokens underwriting them are sold at auction until the premia are paid. If the encumbered uREP is sufficient, then the remaining tokens are returned to the underwriter. If the encumbered uREP is insufficient, then new uREP is minted and sold at market to cover the premia. In this case the entire uDAO suffers because their uREP holdings are diluted, which motivates proper policing in the fourth module Validation Pool.
Advantages[edit | edit source]
Unmanaged interest rates[edit | edit source]
In this decentralized banking scheme, interest is automatically handled. When more people want to save their money (invest), then interest decreases naturally. When more people want to take loans, interest increases. Therefore, there is no need for central planning for banking rates.
Automated optimal actions[edit | edit source]
A sophisticated cfDAO will make the numerical decisions automatic. This is because there are optimal actions based on the subscriber's goals. For example, if the subscriber wishes to use the chit fund as an investment, then the proper bid in any round is given by the formula .
The notation is explained next with a justification for the formula. Denote the number of rounds in the chit fund as . The current stage is . The premium is . The number of subscribers is . (In the basic chit fund .) At each stage the subscribers add to the fund so at each stage . Note that if two or more subscribers have not bid on the fund by the final round, then they split the fund equally.
Assuming the interest rate is positive, is worth more than in the future. Consider the case when there are two bidders who wish to maximize their earnings from the chit fund who are the only ones left to bid in the second to last round. As a rational bidder you should accept on the second to last round, because otherwise you split the same amount later in the final round. So you might as well accept that number earlier. If your opponent underbids you, then you will receive more on the final round. However if you do not bid that low, then your opponent can bid slightly higher than that, diminishing your rewards on the final round. Similar logic applies to the preceding rounds, giving the optimal strategy for an investor is to bid at stage .
For example, if everyone is going to save money the entire time, it's better to get out of the chit fund if you are planning on investing, in order to join another fund that has members who are seeking loan opportunities. So you should always bid on the first round and get out if no one bids low.
Web3 improvements[edit | edit source]
Web3 technology can greatly improve the efficiency and security of the traditional chit fund scheme.
First, a smart contract replaces the organizer, eliminating the risk that the organizer can abscond with the fund. Further, the decreased overhead from automation should typically reduce the 5% organizer commission.
Second, by implementing a subscriber reputational system, honest participation can be tracked across many different chit funds, as people will earn reputation each time they pay their required monthly fee, and lose reputation if they default. The more often they participate honestly, the larger their reputation will grow. Then participation in larger and more complex chit funds can be dependent on reputation, which will incentivize healthy collaboration.
One major source of overhead that makes this subscriber reputation scheme less efficient, is the inevitable possibility of subscribers defaulting on paying the premia. It’s been estimated that 35% of chit fund subscribers have defaulted at least once recently and 24% have defaulted after winning an auction. If a subscriber defaults, their underwriter suffers. If the system which gives subscribers reputation becomes the major reason an underwriter supports their subscribers, then the system will eventually punish underwriters randomly. Because a market for subscriber REP tokens will eventually emerge, and then people will use the tokens to default and make better profit than can be made participating honestly. This suggests that there will always be a need for the current legacy system of KYC rules and legal rules preventing insurance fraud. However, these rules are at the level of the subscriber-underwriter relationship. Not on the level of the DAO, which is supranational.
The advantage of a supranational DAO is that it enhances the core value proposition of banking and insurance--distributing risk across a deep and diverse market. A supranational DAO has a larger, and therefore more stable, capital reserve of equity tokens (underwriter REP) which are measurably valuable according to the market. This decreases the need for cash reserves, making the system more efficient.
If the default risk can be managed at scale, then another advantage is that larger groups dilute the risk of individual default. A chit fund with a large number of people with high reputation can pay smaller premia for insurance. One million people investing $1 daily for 50 years allows 50 people per day to immediately begin taking an average payout of roughly $20,000. More investors investing smaller amounts in shorter increments, means more people can withdraw at any point. By monitoring and analyzing the performance of a fund, programs can suggest values that can be withdrawn at any given time. By automatically bidding when the fund rises above expected levels (as described in the previous section), the fund can be stabilized to give predictable returns. This prediction become more accurate if multiple funds are connected.
With no initial reserve backing, this allows people to bootstrap their way to greater financial security and stability, assuming the reputation system is sufficiently strong to guarantee a low percentage of defaults.
Like other overhead costs (the appeals process, policing, etc.), insurance is cheaper when the system is running well. The more automated the decentralized economy becomes (thanks to smart contracts and optimized UIs, for instance) the less costly insurance is. The purpose of insurance is to decentralize risk. The new tools of information technology and architectures of P2P distributed computing create more effectively decentralized organizations. Decentralizing risk makes insurance more stable and efficient, which improves the function of the economy.