Decentralized underwriting: Difference between revisions
m (→Consequences) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
An Insurance DAO (iDAO) is a DAO devoted to the work of underwriting insurance policies. An iDAO consists of member underwriters who sell insurance policies to non-member customers, creating a decentralized underwriting market.[[Reputation tokenomics|Tokenomics]] formulas give numerical estimations for premia pricing as a function of risk which predicts valuations for the market and the likelihood of iDAO ruin<ref>David C. M. Dickson, (2005) ''Insurance Risk and Ruin'', Cambridge University Press.</ref>, which dictates the capital reserves required for an iDAO.<ref>Craig Calcaterra, Wulf A. Kaal, & Vadhindran K. Rao, (2019) "Decentralized Underwriting". Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3396542 (Retrieved 2023 March 16)</ref> | An Insurance DAO (iDAO) is a DAO devoted to the work of underwriting insurance policies. An iDAO consists of member underwriters who sell insurance policies to non-member customers, creating a decentralized underwriting market. [[Reputation tokenomics|Tokenomics]] formulas give numerical estimations for premia pricing as a function of risk which predicts valuations for the market and the likelihood of iDAO ruin<ref>David C. M. Dickson, (2005) ''Insurance Risk and Ruin'', Cambridge University Press.</ref>, which dictates the capital reserves required for an iDAO.<ref>Craig Calcaterra, Wulf A. Kaal, & Vadhindran K. Rao, (2019) "Decentralized Underwriting". Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3396542 (Retrieved 2023 March 16)</ref> | ||
iDAOs under DGF can be more efficient than traditional insurance companies, since REP tokens in an iDAO can serve as substitutes for capital reserves depending on the degree of decentralization of the iDAO. | iDAOs under DGF can be more efficient than traditional insurance companies, since REP tokens in an iDAO can serve as substitutes for capital reserves depending on the degree of decentralization of the iDAO. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
# Insurance contract ([[Work smart contract]]) | # Insurance contract ([[Work smart contract]]) | ||
# [[Validation Pool]] | # [[Validation Pool]] | ||
# REP-to-BOND market | |||
=== Token scheme === | === Token scheme === | ||
| Line 40: | Line 41: | ||
#* mints REP for <math>U_1</math> proportional to premia & distributes REP salary, or | #* mints REP for <math>U_1</math> proportional to premia & distributes REP salary, or | ||
#* cancels contract, or | #* cancels contract, or | ||
#* pays claim by | #* pays claim by burning encumbered REP and minting sufficient BONDs to cover the claim (REP-to-BOND market) | ||
[[File:IDAO workflow.jpg|border|593x593px]] | [[File:IDAO workflow.jpg|border|593x593px]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
** If the auction price of the encumbered REP is sufficient to cover the claim, and excess cash or REP from the auction is returned to the underwriter. | ** If the auction price of the encumbered REP is sufficient to cover the claim, and excess cash or REP from the auction is returned to the underwriter. | ||
** If the auction price of the encumbered REP is insufficient to cover the claim, further REP is minted and sold at market until the claim is covered. Any excess cash from this process is donated to the iDAO's capital reserve. | ** If the auction price of the encumbered REP is insufficient to cover the claim, further REP is minted and sold at market until the claim is covered. Any excess cash from this process is donated to the iDAO's capital reserve. | ||
* | * The REP-to-BOND market is designed to prevent a [[51% attack]]. When a claim is made, the REP encumbered in the insurance contract is burned. Then [[BOND tokens]], which have no [[Governance|governmental]] power in the DAO, are minted in sufficient quantity to cover the claim. BOND tokens pay off in the future through the REP salary. Through this mechanism a 51% attack is inhibited and the iDAO is strengthened, because only those underwriters who prove competent at issuing insurance contracts according to the standards of the iDAO are given REP power. | ||
== Consequences == | == Consequences == | ||
| Line 134: | Line 135: | ||
There are more issues that can be explored. For example, if there is an increased demand for insurance, as measured by an increase in contracts, which is reflected in an increase in premia and therefore an increase in the REP salary, then the DAO profits increase which means the salary increases. However, since more REP will be minted, a single REP token may not increase in value. [??check against tokenomics formulas.] Based on this, existing contracts may be over-encumbered (or under-encumbered if premia decrease or the market dips). How should we respond? Governance can be made to adjust the requirements based on those market forces. | There are more issues that can be explored. For example, if there is an increased demand for insurance, as measured by an increase in contracts, which is reflected in an increase in premia and therefore an increase in the REP salary, then the DAO profits increase which means the salary increases. However, since more REP will be minted, a single REP token may not increase in value. [??check against tokenomics formulas.] Based on this, existing contracts may be over-encumbered (or under-encumbered if premia decrease or the market dips). How should we respond? Governance can be made to adjust the requirements based on those market forces. | ||
== Economic analysis == | |||
We compare this decentralized scheme with the traditional insurance model, analyzing the microeconomics of supply and demand, moral hazards and adverse selection.<ref>Ray Rees & Achim Wambach (2008) ''The Microeconomics of Insurance'', Now Publishers. | |||
</ref> <ref>Hugh Gravelle & Ray Rees (2006) ''Microeconomics,'' ''3rd ed.'', Pearson.</ref> | |||
== Where we stand practically in deFi == | == Where we stand practically in deFi == | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 24 May 2023
An Insurance DAO (iDAO) is a DAO devoted to the work of underwriting insurance policies. An iDAO consists of member underwriters who sell insurance policies to non-member customers, creating a decentralized underwriting market. Tokenomics formulas give numerical estimations for premia pricing as a function of risk which predicts valuations for the market and the likelihood of iDAO ruin[1], which dictates the capital reserves required for an iDAO.[2]
iDAOs under DGF can be more efficient than traditional insurance companies, since REP tokens in an iDAO can serve as substitutes for capital reserves depending on the degree of decentralization of the iDAO.
Overview
Insurance is essential for every type of business transaction, every type of property, every type of service engaged in business. Every type of economic action is made more efficient when decisions are hedged, so we can be more confident in our investments in the future. We require the trust that the transactions will finalize satisfactorily as planned or that the contract will be made whole by the platform running the marketplace. Decentralized insurance requires networks of policy writers with individual reputations for efficient underwriting of every type of transaction.
Insurance is an essential industry for the modern economy. Like the appeals process of the law, like policing, like the effort to keep track of reputation and maintain the protocols of governance, insurance is an overhead cost that does not directly generate profit. It’s a type of business cost that any efficiency-minded engineer would prefer to eliminate entirely. But inasmuch as we can’t predict the future, insurance will never be eliminated, because it is valuable. Insurance improves the efficiency of the economy by investing in the future, to guarantee the system will continue running, despite inevitable unforeseen problems. Insurance mitigates risk. Insurance helps people get over their fear of joining a transaction because of the risk of loss. In physics jargon, insurance is a catalyst, which provides activation energy for a transaction.
Three important, unintuitive steps in the basic iDAO workflow detailed below, which follows the basic DGF workflow:
- Underwriter gets new REP, instead of cash from premia, for selling a contract.
- All premia are given to the entire iDAO (REP salary), not the underwriter who risks REP.
- A claim is paid by REP market which auctions the particular underwriter’s REP. Underwriter loses REP, not money directly. And the risk is not covered by the entire iDAO, but only the specific underwriter who issues the contract.
Insurance DAO protocols
Components
- iDAO = {Underwriters}
- Underwriter ∋ REP tokens a) Propose contracts with REP b) Police contracts with REP
- Insurance contract (Work smart contract)
- Validation Pool
- REP-to-BOND market
Token scheme
How does an iDAO create and distribute REP tokens and premium cash money from customers?
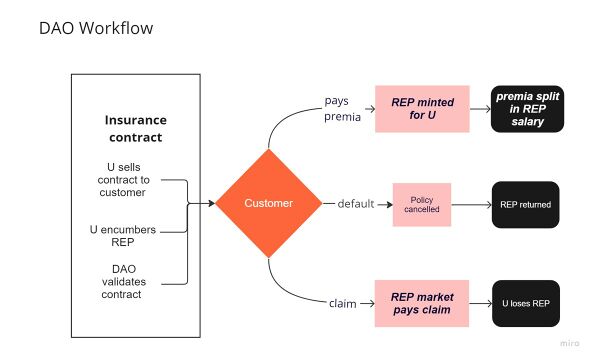
Workflow
(See Figure 1.)
- Underwriter sells a contract to a customer.
- encumbers the canonical amount of REP in the contract.
- Contract Validated by DAO.
- Customer
- pays premia, or
- defaults, or
- claims
- iDAO
- mints REP for proportional to premia & distributes REP salary, or
- cancels contract, or
- pays claim by burning encumbered REP and minting sufficient BONDs to cover the claim (REP-to-BOND market)
Figure 1: iDAO workflow follows basic DGF workflow iterated each time a premium is paid
Notes:
- If a customer makes a claim on the policy, the contract governs how the claim is validated. Typically an oracle and an adjudicator are necessary for this step, which are outside the scope of this specification.
- If a claim is validated, the underwriter's encumbered REP is auctioned at market to pay the claim.
- If the auction price of the encumbered REP is sufficient to cover the claim, and excess cash or REP from the auction is returned to the underwriter.
- If the auction price of the encumbered REP is insufficient to cover the claim, further REP is minted and sold at market until the claim is covered. Any excess cash from this process is donated to the iDAO's capital reserve.
- The REP-to-BOND market is designed to prevent a 51% attack. When a claim is made, the REP encumbered in the insurance contract is burned. Then BOND tokens, which have no governmental power in the DAO, are minted in sufficient quantity to cover the claim. BOND tokens pay off in the future through the REP salary. Through this mechanism a 51% attack is inhibited and the iDAO is strengthened, because only those underwriters who prove competent at issuing insurance contracts according to the standards of the iDAO are given REP power.
Consequences
Properties engendered
- More auditable/transparent than traditional insurance companies, so more trustworthy
- More stable because risk is more decentralized and diversified
- More meritocratic (rewards and punishment are more isolated on the active underwriter)
- Democratized access to participation at all levels
- Incentivizes policing since all members suffer if a contract is insufficiently covered by encumbered REP
- Group doesn’t suffer directly when a claim is made (except loss of future premia). Loss is limited to the underwriter who wrote the contract. In fact, weak underwriting skills is naturally discouraged, since underwriters who choose untrustworthy customers will automatically lose their REP stake.
- Capital reserve holdings can be securely decreased (see below), since the market covers more value than traditional premium pricing models which rely on immediate premium inflows.
Tokenomics
Insurance DAO valuation
In this section, we value REP tokens in an iDAO.
Components
- iDAO ledger of all REP tokens
- Capital reserves
Following basic tokenomics formulas, we make the following definitions:
- the total number of REP tokens in the iDAO at time .
- The rate of total premia that the iDAO earns. Therefore denotes the total fees earned from the beginning of the iDAO until time .
- is the cumulative reputational salary collected for one REP token.
- is the minting ratio.
- is the base discounting rate.
- is the lifetime after which a REP token expires.
Fundamental results
The basic results of REP tokenomics give the present value of a single REP token with finite lifetime . Theorem 3. (Finite Life Tokens)
The total number of active REP tokens at any time is
Actual fees are stochastic, not exponential. is a random variable. So accurately valuating REP is a difficult problem for the market, which depends on the set of all active contracts, health of the marketplace (actuarial statistics), and history of the DAO and the talent of its underwriters in selling contracts. The larger and more decentralized the market, however, the more predictable becomes.
Basic theory of premium pricing makes
Capital reserves can be diminished or eliminated
A capital reserve in a traditional insurance company (AKA an actuarial reserve) is a treasury of liquid cash set aside for future insurance liabilities, to cover all risk beyond the present period’s premia collection.
When a claim is made on an iDAO insurance contract, money can be taken from
- Market for REP tokens. (The encumbered tokens are sold at market for immediate cash to cover the claim. If enough was encumbered, then there is no problem. If it wasn’t enough, then the treasury is necessary, or more REP needs to be minted, which diminishes all members’ REP value.)
- iDAO treasury of capital reserves
#1 gives a new twist on classical ruin theory[4]: The treasury is completely unnecessary if there are enough fees coming in to guarantee the future value of REP is sufficient for the REP market to cover the claim.
This is a provocative proposal: the size of the capital reserves doesn’t need to cover 100% of estimated risk[5], because there is also the value of the equity stock in the company and its market inertia (traditional reputation for doing business even after temporary random setbacks). This is one of the reasons why theoreticians require an insurance firm cover 100% of risk with capital reserves, but in practice, laws in certain insurance realms only require 8-12% of the risk to be covered with the reserve. The value of the company itself covers the other ~90%. We know the company would refinance in case of temporary difficulties. The company would be willing to cover debt for the opportunity to continue working and insuring people. The proof that the company is willing and capable of covering claims even when they are temporarily in the hole gives greater promise of future cash flows, which usually outweighs the debt.
This gap has not been investigated properly. Older companies may deserve to enjoy the gap in full coverage, but younger companies with less track record and less talent and inertia will not deserve the same gap—they should be collateralized 100%. Such regulation should explicitly include that valuation of the company formulaically, not with discrete jump standards imposed by slow governmental bureaucracies.
What makes this obvious in our case is how REP is a hybrid financial tool with 3 functions:
- REP is equity since it gives claims on future DAO profits through the REP salary.
- REP is also a utility token, because it is required to participate in new underwriting.
- REP tokens are essential to the process of covering claims, so it is constantly revaluated through the REP market.
The amount of reserves necessary is dependent on incoming fees (as usual) and future value of existing REP tokens as equity (based primarily on existing contracts and secondarily on the history of the DAO—it’s long-term reputation for doing business, proving it has accumulated talent) and as utility. So, as long as underwriters are doing their jobs, there is then less need for reserves. How much less?
It depends on the existing contracts relative to the quantity of active REP and the risk of those contracts being claimed or defaulting. That depends on many factors, such as the current health of the systems being insured as measured by actuarial statistics and historical inertia. The short answer is, we don’t know. We don’t really know how much an insurance company is worth because of the large amount of risk it covers. It has a high variation, depending on what is happening in the market at the moment—how many claims are being made—and what will happen in the future—how many contracts will be claimed or defaulted in the future.
So even though the provocative proposal above may be valid, it may not be useful if the market does not have enough inertia and decentralization to diversify the risk, giving it enough stability to value the company above 0 for a long enough time to cover its contracts. It is worth analyzing this in greater detail by considering what happens when aggregate fees increase or decrease, which changes the value of REP tokens.
If the fees are stable or increasing faster than interest/inflation , and faster than the valuation at the initiation of a contract, then the tokens are worth more than the estimate and no reserve is necessary assuming the DAO is policing the contracts properly (i.e., the proper amount of REP was encumbered in all contracts to cover the risk). Convrsely, if fees are decreasing, then a reserve may be necessary to prevent a death spiral. So the amount of capital reserves necessary is greater when fees are decreasing faster than predicted at the moment the contracts were valuated. In sum, the size of the reserve required is smaller when the rate of fees are increasing and larger when the rate decreases. This is partially a positive feedback cycle, because if you drop the reserve in good times, then need to save in bad times, that is difficult. Building the reserve when REP is losing its value might lead to the increased perception that REP loses its value. However, that is not correct, because a REP token is a claim on the reserve they are building. So existing REP doesn’t really lose value by building a reserve. It just delays the reward, and loses the relatively minor opportunity cost of holding the liquid cash in reserve for future claims during down periods.
Strangely, if the public loses confidence in the DAO and stops paying premia, then the risk is decreased, since the previous valuations of the encumbered REP are decreased by the loss of premia, but the contracts that defaulted were under-encumbered, so the defaults decreas the risk exposure of the DAO. Any new contracts underwritten with REP can be achieved with the usual market update of the value of REP.
So when premia are decreasing that shrinks the value of REP. The amount of value that the REP loses by fair valuation according to the tokenomics formulas, times the amount of REP encumbered in risky contracts, needs to be covered by depositing the remaining premia in reserve, to the degree that all existing contracts can be covered. Then the iDAO will die if all fees go into the reserve and all the reserve is claimed. In that case the underwriters will lose all their REP value, but the customers would all be covered. That is fair, because that would mean every single contract was claimed, which means the underwriters did a terrible job and deserve to lose their REP. However, that is statistically unlikely in a large DAO. Whoever didn’t have a customer claim on the contracts the underwriter wrote, then the underwriter still has REP and so still has a claim on the remaining reserve, and can still underwrite new contracts or cash out. So the iDAO will continue to live as long as a single underwriter is still doing their job.
This all assumes the market is predictable, which relies partially on the present value formula being predictable. The reserve needs to build when the fees are decreasing and the reserve can shrink and reward underwriters through the REP salary when fees increase. (E.g., increased claims can sometimes decrease the fees, if the insured cancel their policies, or if they are dropped by underwriters who don’t want to continue to insure them, or if underwriters increase their fees.)
So the 0th order state is if the DAO values the contracts properly based on the evidence they have for REP value, then it the DAO remains sound. If they underestimate or overestimate the value, the DAO should build or shrink the reserve—1st order adjustments. 2nd order adjustments may eventually be merited if the DAO become large and stable enough for the measurements to be accurate enough to overcome stochastic errors.
What happens if everyone claims their policy at the same time when a reserve is gone? Then the DAO defaults on the claims, because no one will be getting fees, so the REP will be worthless. So we need to assume the REP market is valuable.
There are more issues that can be explored. For example, if there is an increased demand for insurance, as measured by an increase in contracts, which is reflected in an increase in premia and therefore an increase in the REP salary, then the DAO profits increase which means the salary increases. However, since more REP will be minted, a single REP token may not increase in value. [??check against tokenomics formulas.] Based on this, existing contracts may be over-encumbered (or under-encumbered if premia decrease or the market dips). How should we respond? Governance can be made to adjust the requirements based on those market forces.
Economic analysis
We compare this decentralized scheme with the traditional insurance model, analyzing the microeconomics of supply and demand, moral hazards and adverse selection.[6] [7]
Where we stand practically in deFi
Missing:
- Oracles are not decentralized and efficient
- Adjudication
- Stable coins are not decentralized and/or efficient
- Smart contracts are not efficient
- Local legal regulatory clarity is mostly non-existent
Code
See Also
Notes & References
- ↑ David C. M. Dickson, (2005) Insurance Risk and Ruin, Cambridge University Press.
- ↑ Craig Calcaterra, Wulf A. Kaal, & Vadhindran K. Rao, (2019) "Decentralized Underwriting". Available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3396542 (Retrieved 2023 March 16)
- ↑ Dickson (2005), Chapter 3.
- ↑ Dickson (2005), Chapters 7 & 8.
- ↑ Robin J. Cunningham, Thomas N. Herzog, Richard L. London (2006) Models for Quantifying Risk (2nd ed.), ACTEX Publications.
- ↑ Ray Rees & Achim Wambach (2008) The Microeconomics of Insurance, Now Publishers.
- ↑ Hugh Gravelle & Ray Rees (2006) Microeconomics, 3rd ed., Pearson.